Weiying Zhang - China's First-Order and Second-Order Economic Problems - The Fundamental Role of Opening Up and Market Liberalization - 张维迎 -中国经济的一阶与二阶问题——对外开放和对内放开的根本作用
张维迎:中国经济的一阶问题和二阶问题
EN
Key Logic
Professor Weiying Zhang contends that the core challenge facing the Chinese economy today is not a "Second-Order Problem" at the level of short-term economic policies, but rather a deeper "First-Order Problem" concerning fundamental ideological and institutional choices. He emphasizes that China's economic miracle over the past 40 years has consistently stemmed from resolving "First-Order Problems" such as "Opening Up" and "Market Liberalization," rather than merely relying on fiscal or monetary stimulus. Therefore, to revitalize economic vitality and entrepreneurial confidence, the fundamental solution lies in an unwavering commitment to advancing high-level "Opening Up" and "Market Liberalization," rather than circling around "Second-Order Problems."
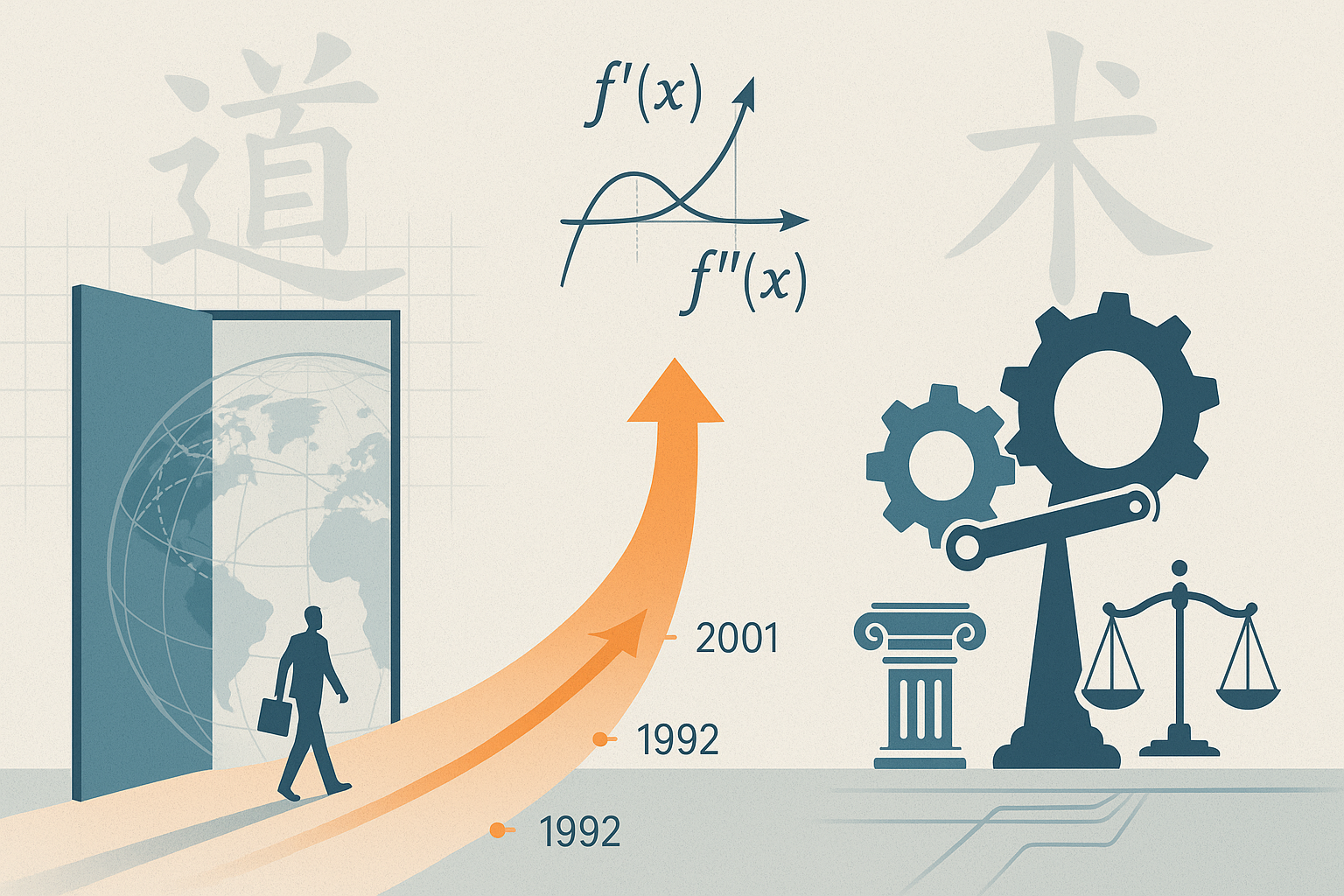
First-Order and Second-Order Problems: Distinction Between Principles and Tactics
- Analogy to Mathematical Concepts:
- First-Order Derivative: Determines the direction of change (increase or decrease).
- Second-Order Derivative: Reflects the rate of change (how fast it increases or decreases).
- Categorization of China's Economic Problems:
- First-Order Problems: Pertain to ideology and institutional models, specifically whether to further deepen the Marketization and Rule of Law processes, or to revert to a Planned Economy and Rule by Man era.
- Second-Order Problems: Involve specific economic policies, such as how to stimulate investment and consumption, or exports, using Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy, and how to address issues in specific industries (e.g., Real Estate).
- Fundamental Distinction: First-order problems represent "principles," while second-order problems represent "tactics."
- Current Focus and Reasons in Economic Discourse:
- Discussions largely focus on second-order problems, while first-order problems are often overlooked.
- Reason One: Cognitive Limitations: Confined by Keynesian Macroeconomics tenets, which suggest that resolving economic downturns involves stimulating investment, boosting consumption, and supporting industries (e.g., Artificial Intelligence or Real Estate).
- Reason Two: Avoidance Strategy: First-order problems are sensitive and difficult to discuss publicly, often assumed not to exist.
- Unsatisfactory Outcomes: Solutions focusing solely on second-order problems have not fundamentally reversed the challenges facing the Chinese economy. Despite frequent policy interventions, entrepreneurial confidence remains low, rooted in the unresolved first-order problems.
CN
Key Logic
张维迎教授认为,当前中国经济面临的核心挑战并非短期经济政策层面的“二阶问题”,而是更深层次的理念和体制选择上的“一阶问题”。他强调,中国过去40多年的经济增长奇迹,均得益于“对外开放”与“对内放开”这两项“一阶问题”的解决,而非单纯的财政或货币刺激。因此,若要重振经济活力和企业家信心,根本之道在于坚定不移地推进高水平的“对外开放”和“对内放开”,而非在“二阶问题”上兜圈子。
一阶问题与二阶问题:道与术的区分
- 数学概念类比:
- 一阶导数:决定变化方向(增加或减少)。
- 二阶导数:反映变化速度(增加或减少的快慢)。
- 中国经济问题分类:
- 一阶问题:关乎理念和体制模式,即是进一步深化Marketization、Rule of Law进程,还是退向Planned Economy、Rule by Man时代。
- 二阶问题:涉及具体的经济政策,如如何用Fiscal Policy和Monetary Policy刺激投资和消费、出口,以及解决特定产业(如Real Estate)问题。
- 本质区别:一阶问题是“道”,二阶问题是“术”。
- 当前经济学界讨论的焦点与原因:
- 多聚焦于二阶问题,一阶问题常被忽视。
- 原因一:认知局限:囿于Keynesian Macroeconomics信条,认为解决经济萧条在于刺激投资、促进消费、扶持产业(如AI或Real Estate)。
- 原因二:回避策略:一阶问题较为敏感,难以公开讨论,常被假定不存在。
- 效果不尽如人意:仅聚焦二阶问题的解决策略未能从根本上扭转中国经济面临的挑战,政策频出,但企业家信心依然不足,其根源在于一阶问题未解决。